In this post, I’m going to tackle the fundamental thing in SEO – SERP, which stands for Search Engine Results Pages. It’s the cutting edge in all modern search engines such as Google, Bing, etc. Search Engine Results Pages are pretty similar throughout all the major search engines. They have the same or similar layout. Plus the same usability principles are put to practice, and there’s a good reason for that. They just found the formula that gives the best results and they’re not going away from it any time soon. As an SEO or a person who would like to know the basics, you need to understand how search engines work and why they look exactly that way.
- Search box – it’s always in the center and in front of everything so that the user can use it as much as possible for doing his searches;
- Search refinements – you have the options to filter your search more precisely. And the option is regularly on the left-hand side because numerous eye-tracking tests show that it is the best place to insert the items that you want the user to definitely notice. The filters allow to segment your search by result types such as images, videos, news, blogs, etc;
- Organic results – these are the results that you get right below the search field when you just use the search engine to find some info. Those results are offered to you based on the relevance to the word or phrase that you originally entered. Each search engine uses its own algorithm for delivering those results but those algos are really similar. And you aim as an SEO is to make your site appear first in those results, if the user searched for your target word. The target word is the one you’re trying to rank high for;
- Paid results – these results are usually on the right hand side on the SERP of. Right at the top of it (right above the organic search results). Such ads are also known as PPC (pay per click ads). An auction system is used to deliver paid results. The position of a particular paid ad is determined by a few factors, such as ad copy relevance, how big was the bid of the advertiser, and the ad copy itself (its content).
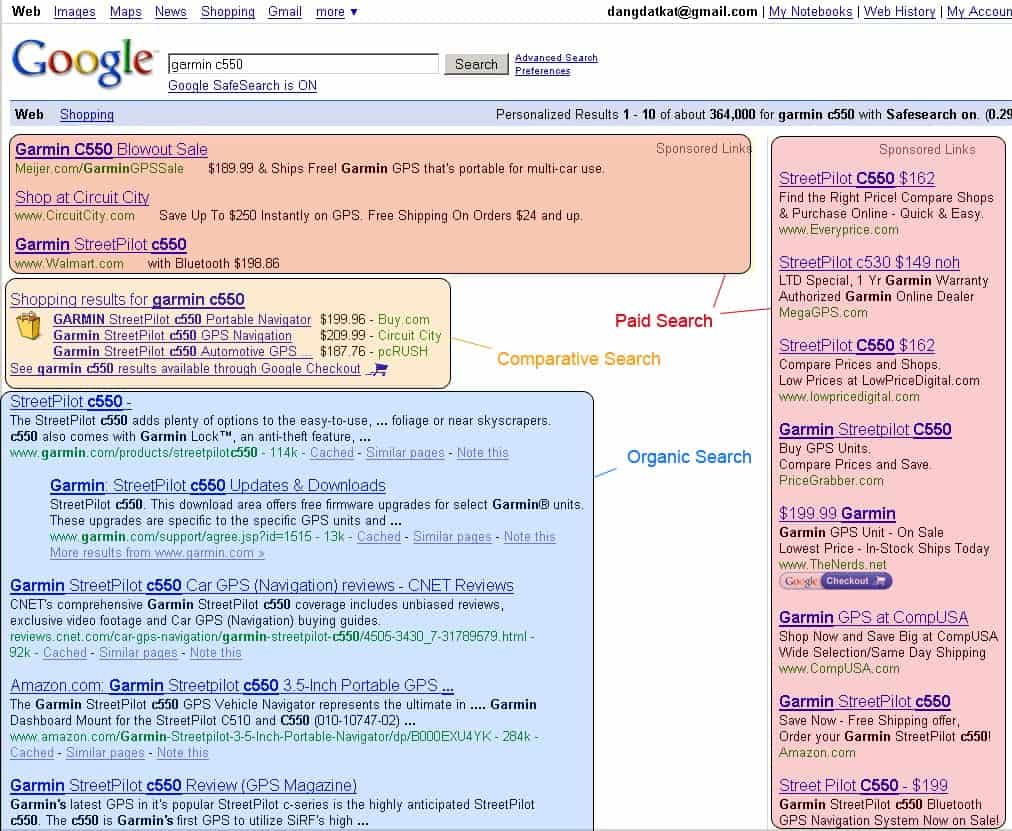
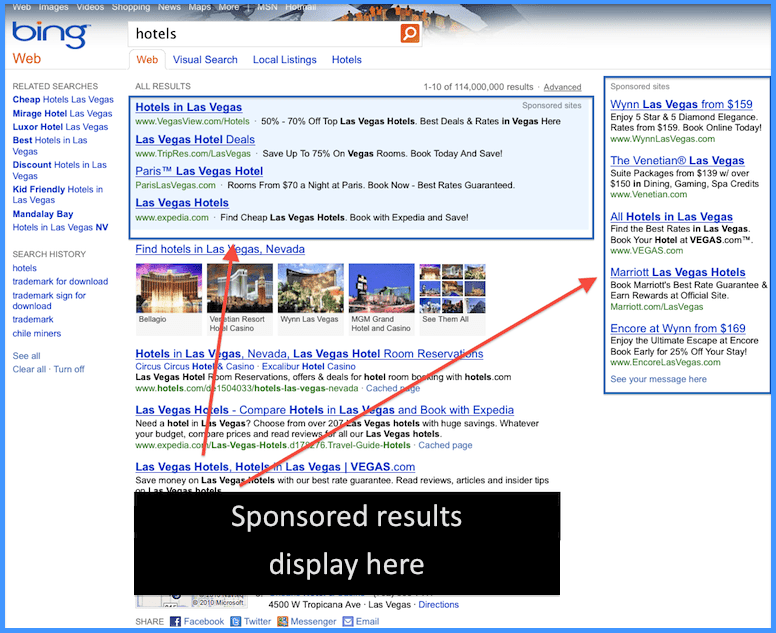
Like I said, SERPs are similar in all the major search engines, You can see that on the screenshots below:
Google SERP
Bing SERP
Yahoo SERP
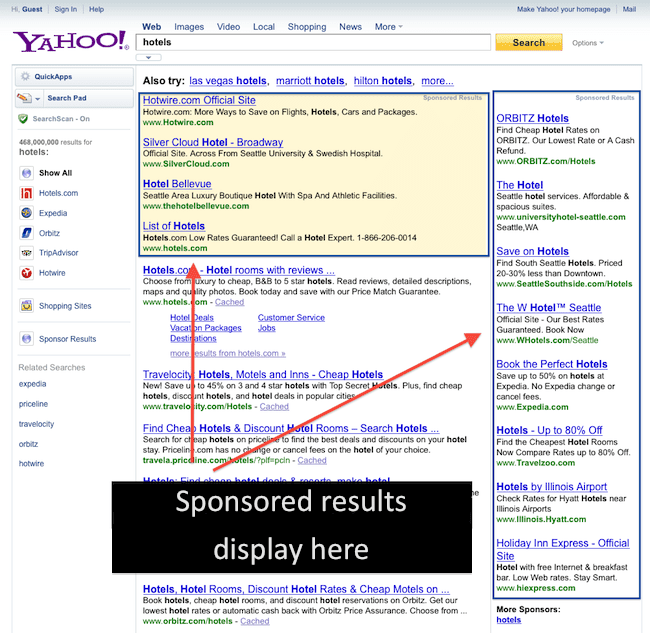
You can easily identify the sections I’ve covered above.
The Spider!
Search engines are constantly indexing (reading and saving on their services) copies of all the sites they can find. They do their best to see what sites have links to what sites. As a matter of fact, it’s not the only factor that search engines use to determine if a site is relevant to a specific search query.

The point is that there are up to 200 factors that are used by the search engines to figure out which exactly site or page has the most relevant content for a given query. Let me mention just a few factors that are used by Google for understanding the relevance of a page: the content of the page, the title of the page, heading, image alt tags and the list goes on and on.
Search engine spiders are doing the actual indexing of sites. No panic! 🙂 They are not actual spiders. As a matter of fact, they are just the computers that were intentionally programmed to wander around the whole Internet, find sites, and record the info from the sites and about the sites. By the way, search engine spiders are sometimes called bots (which is short for robots).
These bots have 2 mains functions:
- Crawling – travelling around the whole web to find sites and links;
- Indexing – creating a database (or an index in other words) of phrases and keywords, sites and actual pages that are relevant to them. Plus the links between them.
What the Index Knows About You
The index contains the following info about web pages:
- the structure and content of a particular page;
- the pages (both external and internal) that have links from this particular page;
- the links that point to this particular page;
- the main HTML tags such as title, heading, and images.
Sure thing, these are just some of the pieces of information that are stored in the index. There are way more things that determine the relationship and relevance between web pages. In order to make things as simple as possible I’m not going to go any further (at least now).
Once the search engine has the above-mentioned info about your web site, it’ll define how relevant your website is to a specific search query. Though there are up to 200 factors that for example Google uses to figure out the relevance for a particular search term, the main factors are:
- the amount, relevance and quality of the sites that link to your site;
- the relevance of your page to the search query the user entered.
Let me repeat that it’s an extremely simplified notion of SEO, but it’s still the one that will help you understand what it is generally all about.
And before I wrap up I’d like to point out one very crucial thing in these regards. You need to keep in mind that external factors (links to your site from other sites) are of by far more importance than links on your site to itself. I’d compare it to the following human behavior pattern. It’s way more valuable and important what other people are saying about you than what you are boasting about yourself. And it’s the same situation with web sites. It’s by far more crucial what and how many other web pages have links pointing to your site.
And that’s how the SEO cookies (Search Engine Results Pages) crumble….
If you have any questions as for SEO, I’d love to answer them. Don’t be shy boys and gals! 🙂